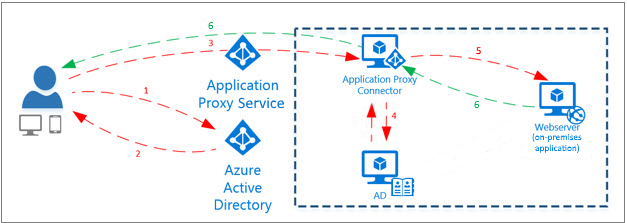
Some time ago i wrote up a post (located here) explaining how you can setup traffic manager with ADFS and have proper monitoring of the service. Today i will go over how to setup ADFS behind the Azure Application Gateway. This will enable you to protect your ADFS service and monitor it with the WAF provided by the application gateway.
- Azure Application Gateway Example
- Application Gateway Pricing | Microsoft Azure
- Availability Sets
- Microsoft Azure Application Gateway
Before we begin one prerequisite which i am still not sure if its really needed but i had problems and i believe this fixed it:
The easiest way to setup an ADFS farm 2016 or 2019 in any of the cloud environments – Azure, AWS or Google GCP is to use our publicly available images in the cloud marketplaces. Setup ADFS Farm 2016 in Azure Deploy a Microsoft ADFS 2016. The ability to open cloud based resources which integrate with Azure Active Directory without having to sign on again has been the domain of ADFS up until this point. With the latest release of Azure AD Connect and Windows 10 1511 on-wards however we can now achieve a similar experience. Deploy Azure AD Connect Health for ADFS. Azure AD Connect Health captures IP addresses recorded in the ADFS logs for bad username/password requests, gives you additional reporting on an array of scenarios, and provides additional insight to support engineers when opening assisted support cases.
You need to set the default HTTPS Binding, i believe this is required as i am not sure if the health probe is truly SNI compliant, i might be wrong here but it doesn’t hurt to set this. To set it you simply need to run the following command on the WAP servers (just change the cert hash):
Steps to deploy AD FS in Azure
The steps mentioned in this section outline the guide to deploy the below depicted AD FS infrastructure in Azure.
1. Deploying the network
As outlined above, you can either create two subnets in a single virtual network or else create two completely different virtual networks (VNet). This article will focus on deploying a single virtual network and divide it into two subnets. This is currently an easier approach as two separate VNets would require a VNet to VNet gateway for communications.
1.1 Create virtual network
In the Azure portal, select virtual network and you can deploy the virtual network and one subnet immediately with just one click. INT subnet is also defined and is ready now for VMs to be added.The next step is to add another subnet to the network, i.e. the DMZ subnet. To create the DMZ subnet, simply
- Select the newly created network
- In the properties select subnet
- In the subnet panel click on the add button
- Provide the subnet name and address space information to create the subnet
1.2. Creating the network security groups
A Network security group (NSG) contains a list of Access Control List (ACL) rules that allow or deny network traffic to your VM instances in a Virtual Network. NSGs can be associated with either subnets or individual VM instances within that subnet. When an NSG is associated with a subnet, the ACL rules apply to all the VM instances in that subnet.For the purpose of this guidance, we will create two NSGs: one each for an internal network and a DMZ. They will be labeled NSG_INT and NSG_DMZ respectively.
After the NSG is created, there will be 0 inbound and 0 outbound rules. Once the roles on the respective servers are installed and functional, then the inbound and outbound rules can be made according to the desired level of security.
After the NSGs are created, associate NSG_INT with subnet INT and NSG_DMZ with subnet DMZ. An example screenshot is given below:
- Click on Subnets to open the panel for subnets
- Select the subnet to associate with the NSG
Azure Application Gateway Example
After configuration, the panel for Subnets should look like below:
1.3. Create Connection to on-premises
We will need a connection to on-premises in order to deploy the domain controller (DC) in azure. Azure offers various connectivity options to connect your on-premises infrastructure to your Azure infrastructure.
- Point-to-site
- Virtual Network Site-to-site
- ExpressRoute
It is recommended to use ExpressRoute. ExpressRoute lets you create private connections between Azure datacenters and infrastructure that's on your premises or in a co-location environment. ExpressRoute connections do not go over the public Internet. They offer more reliability, faster speeds, lower latencies and higher security than typical connections over the Internet.While it is recommended to use ExpressRoute, you may choose any connection method best suited for your organization. To learn more about ExpressRoute and the various connectivity options using ExpressRoute, read ExpressRoute technical overview.
2. Create storage accounts
In order to maintain high availability and avoid dependence on a single storage account, you can create two storage accounts. Divide the machines in each availability set into two groups and then assign each group a separate storage account.
3. Create availability sets
For each role (DC/AD FS and WAP), create availability sets that will contain 2 machines each at the minimum. This will help achieve higher availability for each role.While creating the availability sets, it is essential to decide on the following:
- Fault Domains: Virtual machines in the same fault domain share the same power source and physical network switch. A minimum of 2 fault domains are recommended. The default value is 3 and you can leave it as is for the purpose of this deployment
- Update domains: Machines belonging to the same update domain are restarted together during an update. You want to have minimum of 2 update domains. The default value is 5 and you can leave it as is for the purpose of this deployment
Create the following availability sets
| Availability Set | Role | Fault domains | Update domains |
|---|---|---|---|
| contosodcset | DC/ADFS | 3 | 5 |
| contosowapset | WAP | 3 | 5 |
4. Deploy virtual machines
The next step is to deploy virtual machines that will host the different roles in your infrastructure. A minimum of two machines are recommended in each availability set. Create four virtual machines for the basic deployment.
| Machine | Role | Subnet | Availability set | Storage account | IP Address |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| contosodc1 | DC/ADFS | INT | contosodcset | contososac1 | Static |
| contosodc2 | DC/ADFS | INT | contosodcset | contososac2 | Static |
| contosowap1 | WAP | DMZ | contosowapset | contososac1 | Static |
| contosowap2 | WAP | DMZ | contosowapset | contososac2 | Static |
As you might have noticed, no NSG has been specified. This is because azure lets you use NSG at the subnet level. Then, you can control machine network traffic by using the individual NSG associated with either the subnet or else the NIC object. Read more on What is a Network Security Group (NSG).Static IP address is recommended if you are managing the DNS. You can use Azure DNS and instead in the DNS records for your domain, refer to the new machines by their Azure FQDNs.Your virtual machine pane should look like below after the deployment is completed:
5. Configuring the domain controller / AD FS servers
Application Gateway Pricing | Microsoft Azure
In order to authenticate any incoming request, AD FS will need to contact the domain controller. To save the costly trip from Azure to on-premises DC for authentication, it is recommended to deploy a replica of the domain controller in Azure. In order to attain high availability, it is recommended to create an availability set of at-least 2 domain controllers.
| Domain controller | Role | Storage account |
|---|---|---|
| contosodc1 | Replica | contososac1 |
| contosodc2 | Replica | contososac2 |
- Promote the two servers as replica domain controllers with DNS
- Configure the AD FS servers by installing the AD FS role using the server manager.
6. Deploying Internal Load Balancer (ILB)
6.1. Create the ILB
To deploy an ILB, select Load Balancers in the Azure portal and click on add (+).
Note
if you do not see Load Balancers in your menu, click Browse in the lower left of the portal and scroll until you see Load Balancers. Then click the yellow star to add it to your menu. Now select the new load balancer icon to open the panel to begin configuration of the load balancer.
- Name: Give any suitable name to the load balancer
- Scheme: Since this load balancer will be placed in front of the AD FS servers and is meant for internal network connections ONLY, select 'Internal'
- Virtual Network: Choose the virtual network where you are deploying your AD FS
- Subnet: Choose the internal subnet here
- IP Address assignment: Static
After you click create and the ILB is deployed, you should see it in the list of load balancers:
Next step is to configure the backend pool and the backend probe.
6.2. Configure ILB backend pool
Select the newly created ILB in the Load Balancers panel. It will open the settings panel.
- Select backend pools from the settings panel
- In the add backend pool panel, click on add virtual machine
- You will be presented with a panel where you can choose availability set
- Choose the AD FS availability set
6.3. Configuring probe
In the ILB settings panel, select Health probes.
- Click on add
- Provide details for probea. Name: Probe nameb. Protocol: HTTPc. Port: 80 (HTTP)d. Path: /adfs/probee. Interval: 5 (default value) – this is the interval at which ILB will probe the machines in the backend poolf. Unhealthy threshold limit: 2 (default value) – this is the threshold of consecutive probe failures after which ILB will declare a machine in the backend pool non-responsive and stop sending traffic to it.
We are using the /adfs/probe endpoint that was created explictly for health checks in an AD FS environment where a full HTTPS path check cannot happen. This is substantially better than a basic port 443 check, which does not accurately reflect the status of a modern AD FS deployment. More information on this can be found at https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/applicationproxyblog/2014/10/17/hardware-load-balancer-health-checks-and-web-application-proxy-ad-fs-2012-r2/.
6.4. Create load balancing rules
In order to effectively balance the traffic, the ILB should be configured with load balancing rules. In order to create a load balancing rule,
- Select Load balancing rule from the settings panel of the ILB
- Click on Add in the Load balancing rule panel
- In the Add load balancing rule panela. Name: Provide a name for the ruleb. Protocol: Select TCPc. Port: 443d. Backend port: 443e. Backend pool: Select the pool you created for the AD FS cluster earlierf. Probe: Select the probe created for AD FS servers earlier
6.5. Update DNS with ILB
Using your internal DNS server, create an A record for the ILB. The A record should be for the federation service with the IP address pointing to the IP address of the ILB. For example, if the ILB IP address is 10.3.0.8 and the federation service installed is fs.contoso.com, then create an A record for fs.contoso.com pointing to 10.3.0.8.This will ensure that all data trasmitted to fs.contoso.com end up at the ILB and are appropriately routed.
Warning
If you are using the WID (Windows Internal Database) for your AD FS database, this value should instead be temporarily set to point to your primary AD FS server or the Web Application Proxy will fail enrollement. After you have successfully enrolled all Web Appplication Proxy servers, change this DNS entry to point to the load balancer.
Note
If your deployment is also using IPv6, be sure to create a corresponding AAAA record.
7. Configuring the Web Application Proxy server
7.1. Configuring the Web Application Proxy servers to reach AD FS servers

In order to ensure that Web Application Proxy servers are able to reach the AD FS servers behind the ILB, create a record in the %systemroot%system32driversetchosts for the ILB. Note that the distinguished name (DN) should be the federation service name, for example fs.contoso.com. And the IP entry should be that of the ILB's IP address (10.3.0.8 as in the example).
Warning
If you are using the WID (Windows Internal Database) for your AD FS database, this value should instead be temporarily set to point to your primary AD FS server, or the Web Application Proxy will fail enrollement. After you have successfully enrolled all Web Appplication Proxy servers, change this DNS entry to point to the load balancer.
7.2. Installing the Web Application Proxy role
After you ensure that Web Application Proxy servers are able to reach the AD FS servers behind ILB, you can next install the Web Application Proxy servers.Web Application Proxy servers need not be joined to the domain. Install the Web Application Proxy roles on the two Web Application Proxy servers by selecting the Remote Access role. The server manager will guide you to complete the WAP installation.For more information on how to deploy WAP, read Install and Configure the Web Application Proxy Server.
8. Deploying the Internet Facing (Public) Load Balancer
8.1. Create Internet Facing (Public) Load Balancer
In the Azure portal, select Load balancers and then click on Add. In the Create load balancer panel, enter the following information
- Name: Name for the load balancer
- Scheme: Public – this option tells Azure that this load balancer will need a public address.
- IP Address: Create a new IP address (dynamic)
After deployment, the load balancer will appear in the Load balancers list.
8.2. Assign a DNS label to the public IP
Availability Sets
Click on the newly created load balancer entry in the Load balancers panel to bring up the panel for configuration. Follow below steps to configure the DNS label for the public IP:
- Click on the public IP address. This will open the panel for the public IP and its settings
- Click on Configuration
- Provide a DNS label. This will become the public DNS label that you can access from anywhere, for example contosofs.westus.cloudapp.azure.com. You can add an entry in the external DNS for the federation service (like fs.contoso.com) that resolves to the DNS label of the external load balancer (contosofs.westus.cloudapp.azure.com).
8.3. Configure backend pool for Internet Facing (Public) Load Balancer
Follow the same steps as in creating the internal load balancer, to configure the backend pool for Internet Facing (Public) Load Balancer as the availability set for the WAP servers. For example, contosowapset.
8.4. Configure probe
Follow the same steps as in configuring the internal load balancer to configure the probe for the backend pool of WAP servers.
8.5. Create load balancing rule(s)
Follow the same steps as in ILB to configure the load balancing rule for TCP 443.
9. Securing the network
9.1. Securing the internal subnet
Overall, you need the following rules to efficiently secure your internal subnet (in the order as listed below)
| Rule | Description | Flow |
|---|---|---|
| AllowHTTPSFromDMZ | Allow the HTTPS communication from DMZ | Inbound |
| DenyInternetOutbound | No access to internet | Outbound |
9.2. Securing the DMZ subnet
| Rule | Description | Flow |
|---|---|---|
| AllowHTTPSFromInternet | Allow HTTPS from internet to the DMZ | Inbound |
| DenyInternetOutbound | Anything except HTTPS to internet is blocked | Outbound |
Microsoft Azure Application Gateway
Note
If client user certificate authentication (clientTLS authentication using X.509 user certificates) is required, then AD FS requires TCP port 49443 to be enabled for inbound access.
10. Test the AD FS sign-in
The easiest way is to test AD FS is by using the IdpInitiatedSignon.aspx page. In order to be able to do that, it is required to enable the IdpInitiatedSignOn on the AD FS properties. Follow the steps below to verify your AD FS setup
- Run the below cmdlet on the AD FS server, using PowerShell, to set it to enabled.Set-AdfsProperties -EnableIdPInitiatedSignonPage $true
- From any external machine, access https://adfs-server.contoso.com/adfs/ls/IdpInitiatedSignon.aspx.
- You should see the AD FS page like below:
On successful sign-in, it will provide you with a success message as shown below:

Template for deploying AD FS in Azure
The template deploys a 6 machine setup, 2 each for Domain Controllers, AD FS and WAP.
You can use an existing virtual network or create a new VNET while deploying this template. The various parameters available for customizing the deployment are listed below with the description of usage of the parameter in the deployment process.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | The region to deploy the resources into, e.g. East US. |
| StorageAccountType | The type of the Storage Account created |
| VirtualNetworkUsage | Indicates if a new virtual network will be created or use an existing one |
| VirtualNetworkName | The name of the Virtual Network to Create, mandatory on both existing or new virtual network usage |
| VirtualNetworkResourceGroupName | Specifies the name of the resource group where the existing virtual network resides. When using an existing virtual network, this becomes a mandatory parameter so the deployment can find the ID of the existing virtual network |
| VirtualNetworkAddressRange | The address range of the new VNET, mandatory if creating a new virtual network |
| InternalSubnetName | The name of the internal subnet, mandatory on both virtual network usage options (new or existing) |
| InternalSubnetAddressRange | The address range of the internal subnet, which contains the Domain Controllers and ADFS servers, mandatory if creating a new virtual network. |
| DMZSubnetAddressRange | The address range of the dmz subnet, which contains the Windows application proxy servers, mandatory if creating a new virtual network. |
| DMZSubnetName | The name of the internal subnet, mandatory on both virtual network usage options (new or existing). |
| ADDC01NICIPAddress | The internal IP address of the first Domain Controller, this IP address will be statically assigned to the DC and must be a valid ip address within the Internal subnet |
| ADDC02NICIPAddress | The internal IP address of the second Domain Controller, this IP address will be statically assigned to the DC and must be a valid ip address within the Internal subnet |
| ADFS01NICIPAddress | The internal IP address of the first ADFS server, this IP address will be statically assigned to the ADFS server and must be a valid ip address within the Internal subnet |
| ADFS02NICIPAddress | The internal IP address of the second ADFS server, this IP address will be statically assigned to the ADFS server and must be a valid ip address within the Internal subnet |
| WAP01NICIPAddress | The internal IP address of the first WAP server, this IP address will be statically assigned to the WAP server and must be a valid ip address within the DMZ subnet |
| WAP02NICIPAddress | The internal IP address of the second WAP server, this IP address will be statically assigned to the WAP server and must be a valid ip address within the DMZ subnet |
| ADFSLoadBalancerPrivateIPAddress | The internal IP address of the ADFS load balancer, this IP address will be statically assigned to the load balancer and must be a valid ip address within the Internal subnet |
| ADDCVMNamePrefix | Virtual Machine name prefix for Domain Controllers |
| ADFSVMNamePrefix | Virtual Machine name prefix for ADFS servers |
| WAPVMNamePrefix | Virtual Machine name prefix for WAP servers |
| ADDCVMSize | The vm size of the Domain Controllers |
| ADFSVMSize | The vm size of the ADFS servers |
| WAPVMSize | The vm size of the WAP servers |
| AdminUserName | The name of the local Administrator of the virtual machines |
| AdminPassword | The password for the local Administrator account of the virtual machines |